Important Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry
Important Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry
Some Applications of Trigonometry Class 10 Important Questions Very Short Answer (1 Mark)
Question 1.
A ladder 15 m long just reaches the top of a vertical wall. If the ladder makes an angle of 60° with the wall, then calculate the height of the wall. (2013OD)
Solution:
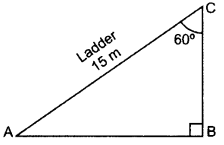
∠BAC = 180° – 90° – 60o = 30°
sin 30° = BCAC
12=BC15
2BC = 15
BC = 152m
Question 2.
In the given figure, a tower AB is 20 m high and BC, its shadow on the ground, is 203–√ m long. Find the Sun’s altitude. (2015OD)
Solution:
AB = 20 m, BC = 203–√ m,
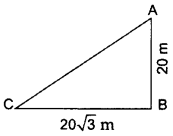
θ = ?
In ∆ABC,

Question 3.
In the figure, AB is a 6 m high pole and CD is a ladder inclined at an angle of 60° to the horizontal and reaches up to a point D of pole. If AD = 2.54 m. Find the length of the ladder. (Use 3–√ = 1.73) (2016D)
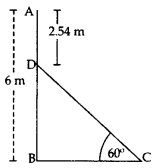
Solution:
BD = AB – AD = 6 – 2.54 = 3.46 m
In rt., ∆DBC, sin 60° = BDDC
3√2=3.46DC
3–√DC = 3.46 x 2
∴ Length of the ladder, DC = 6.923√=6.921.73
DC = 4 m
Question 4.
A ladder, leaning against a wall, makes anangle of 60° with the horizontal. If the foot of the ladder is 2.5 m away from the wall, find the length of the ladder. (2016OD)
Solution:
Let AC be the ladder
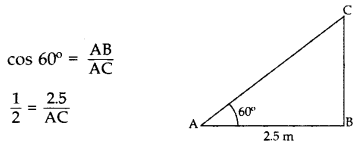
∴ Length of ladder, AC = 5 m 2.5 m
Question 5.
If a tower 30 m high, casts a shadow 103–√ m long on the ground, then what is the angle of elevation of the sun? (2017OD)
Solution:
Let required angle be θ.
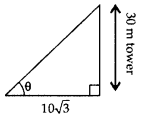
tan θ = 30103√
tan θ = 3–√
⇒ tan θ = tan 60° ∴ θ = 60°
Question 6.
The tops of two towers of height x and y, standing on level ground, subtend angles of 30° and 60° respectively at the centre of the line joining their feet, then find x : y. (2015D)
Solution:
When base is same for both towers and their heights are given, i.e., x and y respectively
Let the base of towers be k.
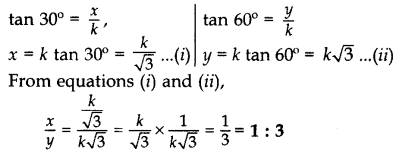
Some Applications of Trigonometry Class 10 Important Questions Short Answer-I (2 Marks)
Question 7.
The angles of depression of two ships from the top of a light house and on the same side of it are found to be 45° and 30°. If the ships are 200 m apart, find the height of the light house. (2012D)
Solution:
Let AB be the height of the light house,
D and C are two ships and DC = 200 m
Let BC = x m, AB = h m
In rt. ∆ABC,
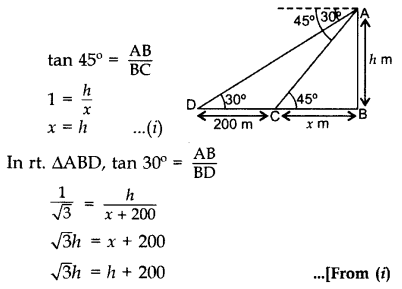
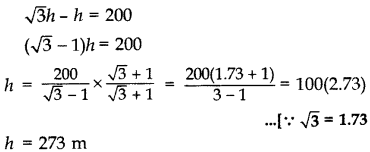
∴ Height of the light house = 273 m
Question 8.
The horizontal distance between two poles is 15 m. The angle of depression of the top of first pole as seen from the top of second pole is 30°. If the height of the second pole is 24 m, find the height of the first pole. [Use 3–√ = 1.732] (2013D)
Solution:
Let AB be the 1st pole
and CE = 24 m be the 2nd pole
In ∆ADE,
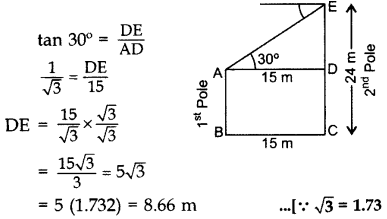
∴ Height of the first pole,
AB = CD = CE – DE
= 24 – 8.66 = 15.34 m
Question 9.
As observed from the top of a 60 m high light house from the sea-level, the angles of depression of two ships are 30° and 45°. If one ship is exactly behind the other on the same side of the light-house, find the distance between the two ships. (Use 3–√ = 1.732] (2013OD)
Solution:
Let AB = 60 m be the height of Light-house and C and D be the two ships.
In right ∆ABC,
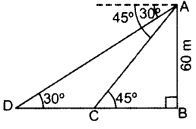
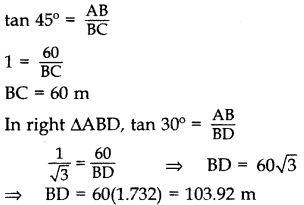
∴ Distance between the two ships,
CD = BD – BC = 103.92 – 60 = 43.92 m
Question 10.
Two ships are there in the sea on either side of a light house in such a way that the ships and the light house are in the same straight line. The angles of depression of two ships as observed from the top of the light house are 60° and 45°. If the height of the light house is 200 m, find the distance between the two ships. [Use 3–√ = 1.73] (2014D)
Solution:
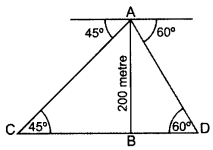
Let AB be the light house and C and D be the two ships,
In rt. ∆ABC, tan 45° = ABBC
Question 11.
The angle of elevation of an aeroplane from a point on the ground is 60°. After a flight of 30 seconds the angle of elevation becomes 30°. If the aeroplane is flying at a constant height of 30003–√ m, find the speed of the aeroplane. (2014OD)
Solution:
Let A be the point on the ground and C be the aeroplane.
In rt. ∆ABC,


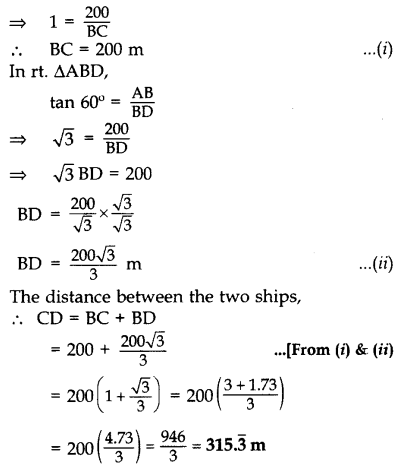
Question 12.
From the top of a 60 m high building, the angles of depression of the top and the bottom of a tower are 45° and 60° respectively. Find the height of the tower. (Take 3–√ = 1.73] (2014OD)
Solution:
Let AC be the building & DE be the tower.
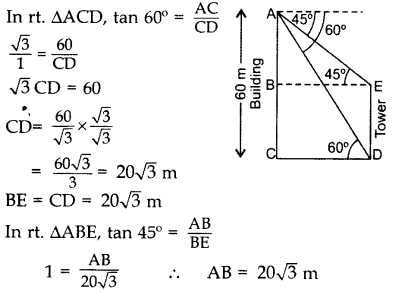
∴ Height of the tower, DE = BC
DE = AC – AB
DE = 60 – 203–√ = 20(3 – 3–√)
DE = 20(3 – 1.73) = 20(1.27)
DE = 25.4 m
Question 13.
The angle of elevation of the top of a building from the foot of the tower is 30° and the angle of elevation of the top of the tower from the foot of the building is 45°. If the tower is 30 m high, find the height of the building. (2015D)
Solution:
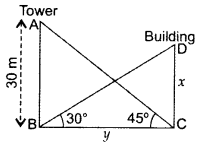
Let height of building be x and the distance between tower and building be y.
In ∆ABC,

∴Height of the building is 103–√ m.
Question 14.
The angle of elevation of an aeroplane from a point A on the ground is 60°. After a flight of 15 seconds, the angle of elevation changes to 30°. If the aeroplane is flying at a constant height of 15003–√ m, find the speed of the plane in km/hr. (2015OD)
Solution:
Let AL = x, BL = CM = 15003–√
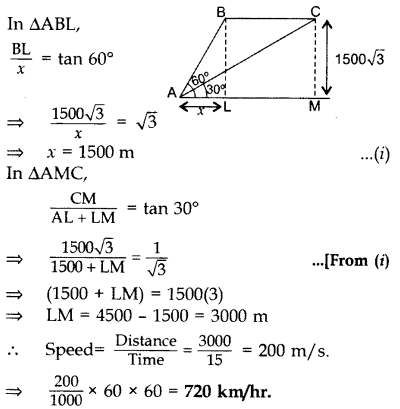
Question 15.
The angles of depression of the top and bottom of a 50 m high building from the top of a tower are 45° and 60° respectively. Find the height of the tower and the horizontal distance between the tower and the building. [Use 3–√ = 1.73]. (2016D)
Solution:
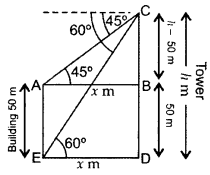
Let AE be the building and CD be the tower. Let height of the tower = h m
and, the horizontal distance between tower and building = x m …[Given
BD = AE = 50 m
∴ BC = CD – BD = (h – 50) m
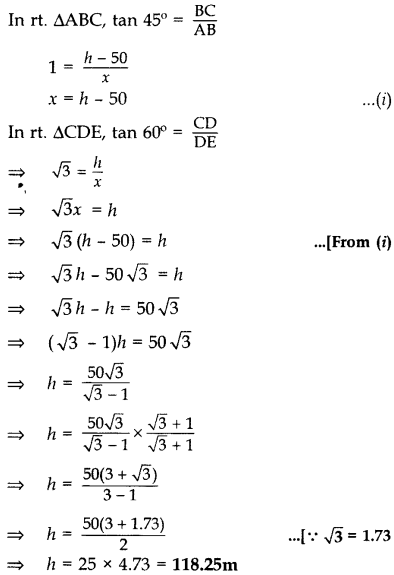
From (i), x = h – 50
= 118.25 – 50 = 68.25 m
Height of the tower, h = 118.25 m
∴ Horizontal distance between tower and Building, x = 68.25 m
Question 16.
A man standing on the deck of a ship, which is 10 m above water level, observes the angle of elevation of the top of a hill as 60° and the angle of depression of the base of hill as 30°. Find the distance of the hill from the ship and the height of the hill. (2016D)
Solution:
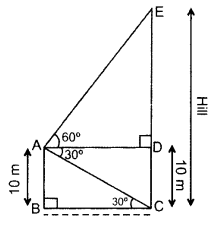
Let the man standing on the deck of a ship be at point A and let CE be the hill.
Here BC is the distance of hill from ship and CE be the height of hill.
In rt. ∠ABC, tan 30° = ABBC
BC = 103–√ m .(i)
BC = 10(1.73) = 17.3 m …[:: 3–√ = 1.73
AD = BC = 10 3–√ m …(ii) [From (i)
In rt. ∆ADE, tan 60° = DEAD
⇒ 3–√=DE103√ … [From (ii)
⇒ DE = 103–√ × 3–√ = 30 m
∴ CE = CD + DE = 10 + 30 = 40 m
Hence, the distance of the hill from the ship is 17.3 m and the height of the hill is 40 m.
Some Applications of Trigonometry Class 10 Important Questions Long Answer (4 Marks)
Question 17.
The angle of elevation of the top of a vertical tower from a point on the ground is 60°. From another point 10 m vertically above the first, its angle of elevation is 30°. Find the height of the tower. (2011OD)
Solution:
Let AC be the tower
Let AC = y m
Let DC = EB = x m
In rt. ∆ABE,
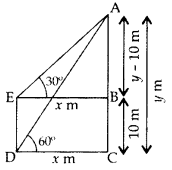
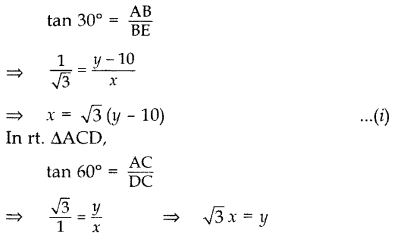
3–√.3–√ (y – 10) = y … [From (i)
3(y – 10) = y ⇒ 3y – 30 = y
3y – y = 30 ⇒ 2y = 30
∴ Height of the tower, y = 15 m
Question 18.
From the top of a tower 100 m high, a man observes two cars on the opposite sides of the tower with angles of depression 30° and 45° respectively. Find the distance between the cars. (Use 3–√ = 1.732] (2011D)
Solution:
Let AB be the tower.
In rt. ∆ABC, tan 45° = ABBC
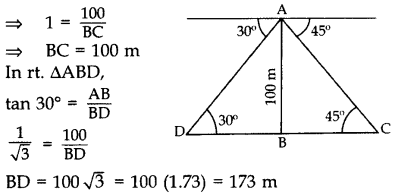
∴ Distance between the cars, CD
= BD + BC
= 173 + 100
= 273 m
Question 19.
Two poles of equal heights are standing opposite to each other on either side of the road, which is 100 m wide. From a point between them on the road, the angles of elevation of the top of the poles are 60° and 30° respectively. Find the height of the poles. (2011D)
Solution:
Let AB and DE be the two equal poles and C be the point on BD (road).
Let BC = x m
Then CD = (100 – x) m
Let AB = DE = y m
In rt. ∆ABC,
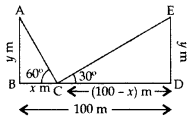
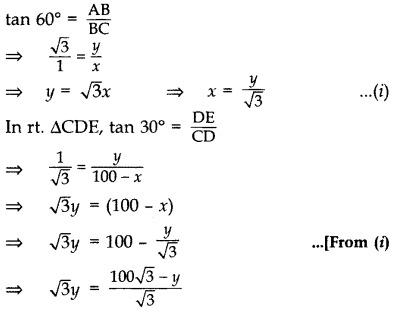
⇒ 3y = 1003–√ – y
⇒ 4y = 1003–√
∴ Height of the poles,
y = 1003√4 = 253–√ m = 25(1.73) = 43.25 m
Question 20.
From a point on the ground, the angles of elevation of the bottom and top of a transmission tower fixed at the top of a 10 m high building are 30° and 60° respectively. Find the height of the tower. (2011D)
Solution:
Let BC be the building and CD be the transmission tower. A be the point on the ground.
Let CD = y m
In rt. ∆ABC,
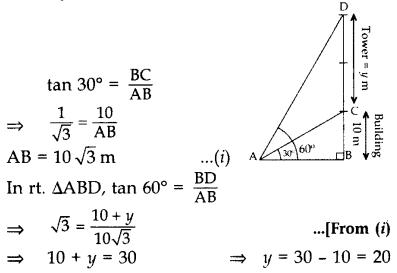
∴ Height of transmission tower = 20 m
Question 21.
From the top of a vertical tower, the angles of depression of two cars, in the same straight line with the base of the tower, at an instant are found to be 45° and 60°. If the cars are 100 m apart and are on the same side of the tower, find the height of the tower. [Use 3–√ = 1.732] (2011OD)
Solution:
Let AB be the tower
Let AB = h m,
and BC = x m
In rt. ∆ABC,
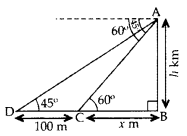
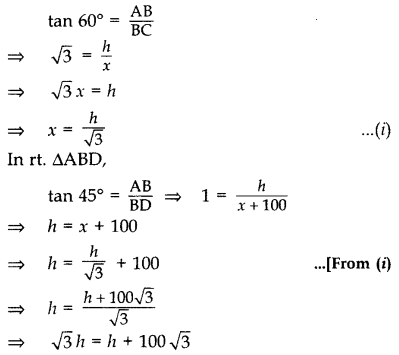
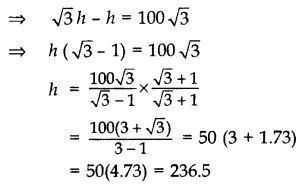
∴ Height of the tower, h = 236.5 m
Question 22.
The angles of depression of the top and bottom of a 12 m tall building, from the top of a multi-storeyed building are 30° and 60° respectively. Find the height of the multistoreyed building. (2011OD)
Solution:
Let AC be the multi-storeyed building and DE be the other building.
Let AC = y m,
DC = EB = x m
In rt. ∆ABE,
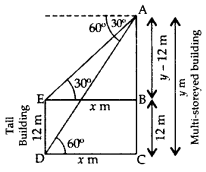
tan 30° = ABBE
13√=y−12x
x = 3–√(y – 12)
In rt. ∆ACD, tan
60° = ACDC
⇒ 3√1=yx
⇒ 3–√x = y
⇒ 3–√.3–√ (y – 12) = y … [From (i)
⇒ 3 (y – 12) = y
⇒ 3y – 36 = y
⇒ 3y – y = 36
⇒ 2y = 36
⇒ y = 18
∴ Height of the multi-storeyed building, y = 18 m
Question 23.
The angle of elevation of the top of a building from the foot of a tower is 30° and the angle of elevation of the top of the tower from the foot of the building is 60°. If the tower is 50 m high, find the height of the building. (2011OD)
Solution:
Let AB = 50 m be the tower
and CD be the building.
In rt. ∆ABC,


Question 24.
The angle of elevation of the top of a hill at the foot of a tower is 60° and the angle of depression from the top of the tower of the foot of the hill is 30°. If the tower is 50 m high, find the height of the hill. (2012D)
Solution:
Let CD = H m, be the height of the hill
AB = 50 be the tower
and Distance between them, BC = x m
In rt. ∆ABC,
tan 30° = ABBC
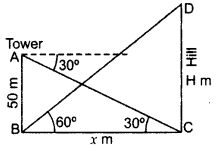
13√=50x
x = 503–√
In rt. ∆BCD,
tan 60° = CDBC
3–√ = H503√ ⇒ H = 503–√ × 3–√ = 150
∴ Height of the hill = 150 m
Question 25.
From the top of a hill, the angles of depression of two consecutive kilometre stones due east are found to be 30° and 45°. Find the height of the hill. (2012D)
Solution:
Let AB be the hill of height h km.
Let C and D be two stones due east of the hill at a distance of 1 km from each other.
Let BC = x km
In rt. ∆ABC,
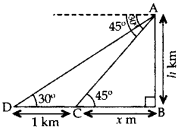
tan 45° = ABBC
= 1 = hx
= h = x … (1)
In rt. ∆ABD, tan 30° = ABBD
13√=hx+1
3–√h = x + 1
3–√x = x + 1 …[From (i)
3–√x – x = 1
(3–√ – 1)x = 1

Hence, the height of the hill is 1.365 km.
Question 26.
The shadow of a tower standing on a level ground is found to be 20 m longer when the Sun’s altitude is 45° than when it is 60°. Find the height of the tower. (2012D)
Solution:
Let AB be the tower = h m
BC = x m, DC = 20 m
In rt. ∆ABC, tan 60° = ABBC
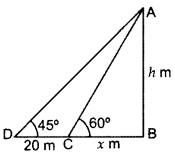

∴ Height of the tower = 47.3 m
Question 27.
A kite is flying at a height of 45 m above the ground. The string attached to the kite is temporarily tied to a point on the ground. The inclination of the string with the ground is 60°. Find the length of the string assuming that there is no slack in the string. (2012D )
Solution:
Let AB = 45 m be the height of the kite from the ground,
In rt. ∆ABC, sin 60° = ABAC
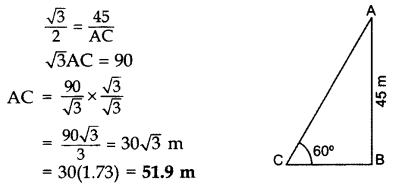
Question 28.
The angles of depression of the top and bottom of a tower as seen from the top of a 603–√ m high cliff are 45° and 60° respectively. Find the height of the tower. (2012D)
Solution:
Let AB = 603–√ be the cliff and CD be the tower.
In rt. ∆ABC,
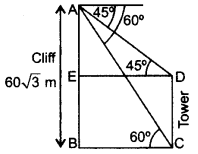
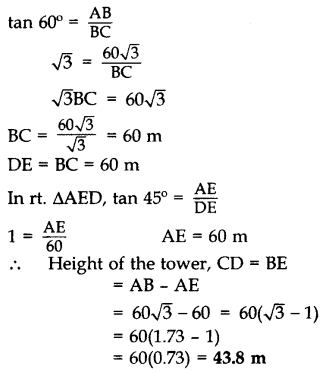
Question 29.
The angles of elevation and depression of the top and bottom of a light-house from the top of a 60 m high building are 30° and 60° respectively. Find:
(i) the difference between the heights of the light-house and the building.
(ii) the distance between the light-house and the building. (2012OD)
Solution:
Let AB = 60 m be the building
and CE be the light-house.
In rt. ∆ABC,
tan 60° = ABBC
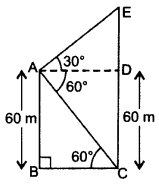


∴ (i) Difference between the heights = 20 m
and (ii) Distance = 34.64 m
Question 30.
The angle of elevation of the top of a building from the foot of the tower is 30° and the angle of elevation of the top of the tower from the foot of the building is 60°. If the tower is 60 m high, find the height of the building. (2013D)
Solution:
Let AB = 60 m be the tower
and let CD be the building.
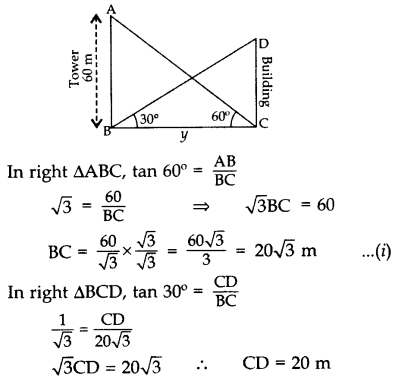
∴Height of the building, CD = 20 m
Question 31.
From a point P on the ground, the angle of elevation of the top of a 10m tall building is 30°. A flagstaff is fixed at the top of the building and the angle of elevation of the top of the flagstaff from P is 45°. Find the length of the flagstaff and the distance of the building from the point P. (Take 3–√ = 1.73) (2013D)
Solution:
Let QR = 10 m be the building
and RS be the flagstaff.
In right ∆PQR,
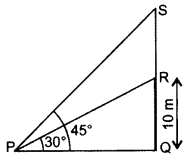

Length of the flagstaff, RS = 17.3 – 10
= 7.3 m
Question 32.
Two poles of equal heights are standing opposite each other on either side of the road, which is 80 m wide. From a point between them on the road, the angles of elevation of the top of the poles are 60° and 30° respectively. Find the height of the poles and the distances of the point from the poles. (2013D)
Solution:
Let AB = DE = y m be the two poles such that
BD = 80 m, CD = x m and BC = 80 – x m
In rt. ∆CDE,
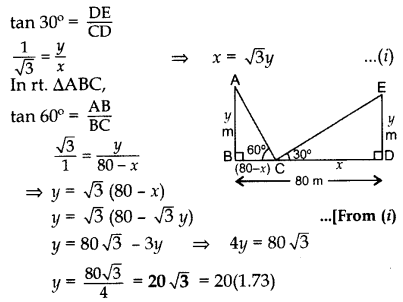
Height of pole = 34.6 m
Puting the value of y in (i),
x = 3–√ (203–√) ∴ x = 60
∴ CD, x = 60 m
Distance of poin from the pole
and BC = 80 – x = 80 – 60 = 20 m
Question 33.
The angle of elevation of the top of a building from the foot of a tower is 30°. The angle of elevation of the top of the tower from the foot of the building is 60°. If the tower is 60 m high, find the height of the building. (2013OD)
Solution:
Refer to Question 30, Page 143.
Question 34.
The angles of elevation and depression of the top and the bottom of a tower from the top of a building, 60 m high, are 30° and 60° respectively. Find the difference between the heights of the building and the tower and the distance between them. (2014D)
Solution:
Let AB be the building and CE be the tower.
In rt. ∆ABC, tan 60° = ABAC
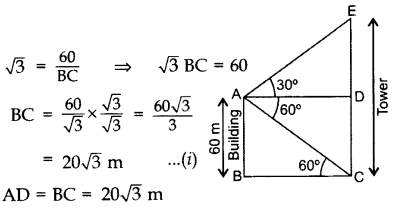

∴ Difference between the heights of the building and the tower, DE = 20 m
Distance between them,
BC= 203–√m = 20(1.73) = 34.6 m
Question 35.
A peacock is sitting on the top of a pillar, which is 9 m high. From a point 27 m away from the bottom of the pillar, a snake is coming to its hole at the base of the pillar. Seeing the snake the peacock pounces on it. If their speeds are equal, at what distance from the hole is the snake caught? (2014D)
Solution:
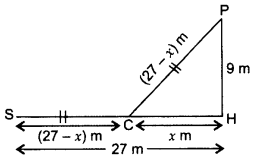
Lęt PH be the pillar. Let the distance from the hole to the place where snake is caught = x m
Let P be the top of the pillar and S be the point where the snake is
∴ SC = (27 – x)m
SC = PC = (27 – x)m …[∵ Their speeds are equal
In rt. ∆PHC
PH2 + CH2 = PC2 …[Pythagoras’ theorem
92 + x2 = (27 – x)2
81 + x2 = 729 – 54x + x2
54x = 729 – 81 = 648
x = 64854 = 12 m
Hence, required distance, x =12 m
Question 36.
The angle of elevation of the top of a tower at a distance of 120 m from a point A on the ground is 45°. If the angle of elevation of the top of a flagstaff fixed at the top of the tower, at A is 60°, then find the height of the flagstaff. (Use 3–√ = 1.732] (2014OD)
Solution:
Let BC be the tower
and CD be the flagstaff.
In rt. ∆ABC, tan 45° = BCAB
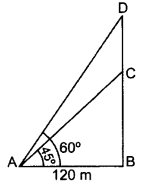
1 = BC120
BC = 120 m …(i)
In rt. ∆ABD,
tan 60° = BDAB
3–√ = BD120
BD = 120 3–√ …(ii)
Height of the flagstaff,
CD = BD – BC
= 1203–√ – 120
= 120(3–√ – 1)
= 120(1.73 – 1)
= 120(0.73) = 87.6 m
Question 37.
From a point P on the ground the angle of elevation of the top of a tower is 30° and that of the top of a flag staff fixed on the top of the tower, is 60°. If the length of the flag staff is 5m, find the height of the tower. (2015D)
Solution:
In ABCD,
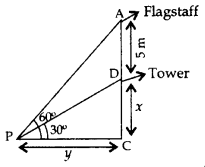
(i) xy = tan 30° = 13√
y = 3–√x ..(i)
In ∆ABC,
(ii) x+5y = tan 60°
tan 60° = 3–√
x+53√x = 3–√ …[From (i)
⇒ 3x = x + 5 or x = 2.5
∴ Height of Tower = x = 2.5 m
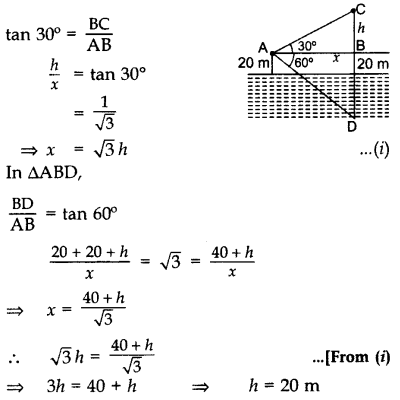
Question 38.
At a point A, 20 metres above the level of water in a lake, the angle of elevation of a cloud is 30°. The angle of depression of the reflection of the cloud in the lake, at A is 60°. Find the distance of the cloud from A. (2015OD)
Solution:
In ∆ABC
Putting the value of h in equation (i),
∴ x = 203–√ m
Using pythagoras’ theorem,
AC = (h)2+(x)2−−−−−−−−−√
∴ AC = (20)2+(203–√)2−−−−−−−−−−−−−√ = 40 m
Distance of the cloud from A = 40 m.
Question 39.
The angle of elevation of a cloud from a point 60 m above the surface of the water of a lake is 30° and the angle of depression of its shadow in water of lake is 60°. Find the height of the cloud from the surface of water. (2017D)
Solution:
Let the height of the cloud from the surface of lake EC = H m = EF (image in water)
and A be the point, the distance between A and perpendicular of cloud AD = x m
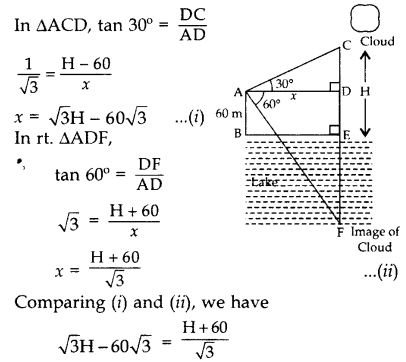
⇒ 3H – 180 = H + 60
⇒ 3H – H = 60 = 180
⇒ 2H = 240
⇒ H = 120
∴ Height of the cloud = 120 m
Question 40.
A bird is sitting on the top of a 80 m high tree. From a point on the ground, the angle of elevation of the bird is 45°. The bird flies away horizontally in such a way that it remained at a constant height from the ground. After 2 seconds, the angle of elevation of the bird from the same point is 30°. Find the speed of flying of the bird. (Take 3–√ = 1.732) (2016D)
Solution:
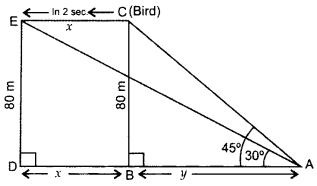
Let BC be the tree
In rt. ∆ABC, tan 45° = BCAB
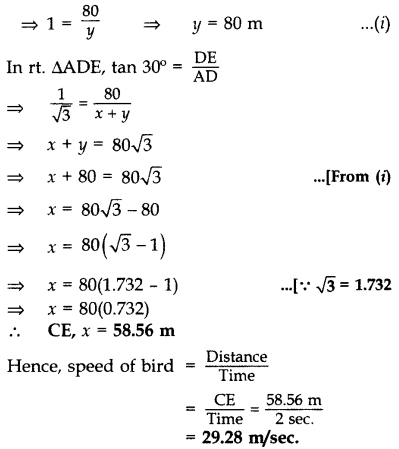
Question 41.
The angles of elevation of the top of a tower from two points at a distance of 4 m and 9 m from the base of the tower and in the same straight line with it are 60° and 30° respectively. Find the height of the tower. (2016D)
Solution:
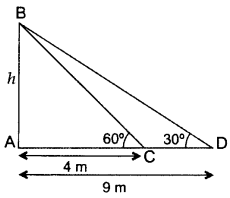
Let the height of the tower, AB = h m
In ∆ABC, tan 60° = ABAC
3–√ = h4 ⇒ h = 43–√
Hence, height of the tower = 473 m
Question 42.
The angle of elevation of the top of a vertical tower PQ from a point X on the ground is 60°. From a point Y, 40 m vertically above X, the angle of elevation of the top Q of tower is 45°. Find the height of the tower PQ and the distance PX. (Use 3–√ = 1.732) (2016 OD)
Solution:
Let QR = x m
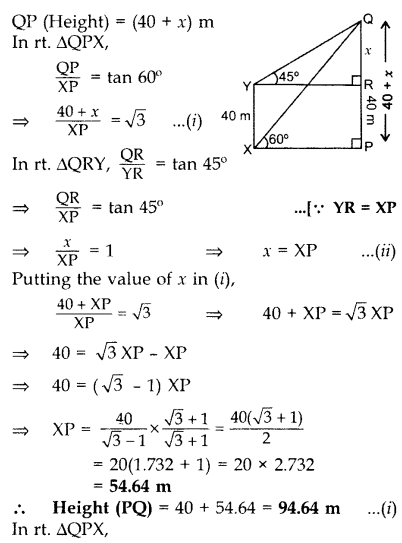
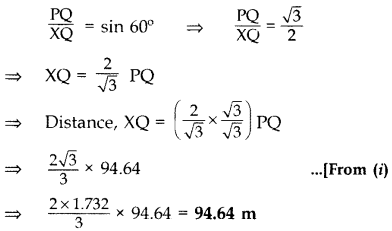
Hence, height of the tower PQ is 96.54 m and the distance PX is 109.3 m.
Question 43.
As observed from the top of a light house, 100 m high above sea level, the angles of depression of a ship, sailing directly towards it, changes from 30° to 60°. Find the distance travelled by the ship during the period of observation. (Use 3–√ = 1.732) (2016OD)
Solution:
Let AB = 100 m be the light-house and B, C be the two positions of the ship and CD be the distance travelled by ship.
In rt. ∆ABC, tan 60° = ABBC
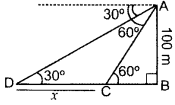
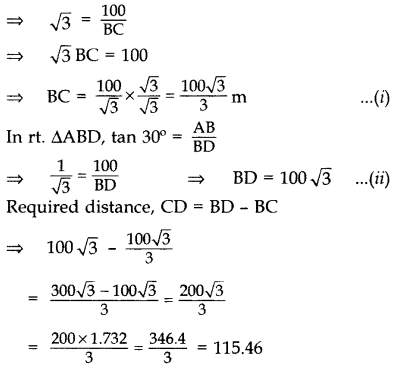
∴ Distance travelled by ship is 115.46 m
Question 44.
An aeroplane is flying at a height of 300 m above the ground. Flying at this height, the angles of depression from the aeroplane of two points on both banks of a river in opposite directions are 45o and 60° respectively. Find the width of the river. [Use 3–√ = 1.732] (2017OD)
Solution:
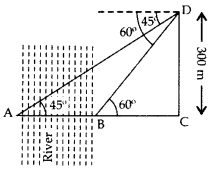
Let CD be height of an aeroplane flying above the ground and AB be the two banks of the river.
In rt. ∆BCD, tan 60° = CDBC
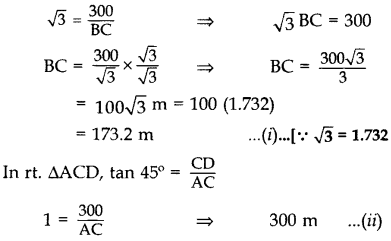
The width of the river, AB = AC – BC
= 300 – 173.2
= 126.8 m
Question 45.
From a point on the ground, the angle of elevation of the top of a tower is observed to be 60°. From a point 40 m vertically above the first 300 AC point of observation, the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is 30°. Find the height of the tower and its horizontal distance from the point of observation. (2016OD)
Solution:
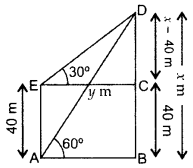
Let BD be the tower, i.e., x m.
In rt. ∆ABD, tan 60° = BDAB
![]()
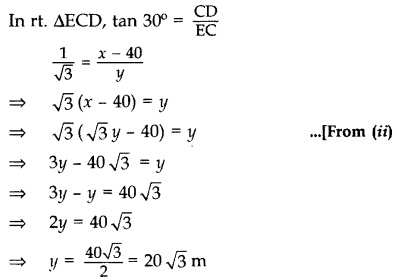
From (i) x = 3–√ (203–√) = 60 m
∴Height of the tower, r = 60 m
Required horizontal distance, y = 203–√m
y = 20(1.73) = 34.6 m …[∵ 3–√ = 1.73
