NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.1
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.1
Get Free NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Ex 3.1 PDF. Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions are extremely helpful while doing your homework. Exercise 3.1 Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions were prepared by Experienced LearnCBSE.in Teachers. Detailed answers of प्रश्नावली 3.1 का हल हिंदी में Class 10 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Exercise 3.1 provided in NCERT TextBook.
Topics and Sub Topics in Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables:
| Section Name | Topic Name |
| 3 | Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables |
| 3.1 | Introduction |
| 3.2 | Pair Of Linear Equations In Two Variables |
| 3.3 | Graphical Method Of Solution Of A Pair Of Linear Equations |
| 3.4 | Algebraic Methods Of Solving A Pair Of Linear Equations |
| 3.4.1 | Substitution Method |
| 3.4.2 | Elimination Method |
| 3.4.3 | Cross-Multiplication Method |
| 3.5 | Equations Reducible To A Pair Of Linear Equations In Two Variables |
| 3.6 | Summary |
- Pair Of Linear Equations In Two Variables Class 10 Ex 3.1
- प्रश्नावली 3.1 का हल हिंदी में
- Pair Of Linear Equations In Two Variables Class 10 Ex 3.2
- प्रश्नावली 3.2 का हल हिंदी में
- Pair Of Linear Equations In Two Variables Class 10 Ex 3.3
- प्रश्नावली 3.3 का हल हिंदी में
- Pair Of Linear Equations In Two Variables Class 10 Ex 3.4
- प्रश्नावली 3.4 का हल हिंदी में
- Pair Of Linear Equations In Two Variables Class 10 Ex 3.5
- प्रश्नावली 3.5 का हल हिंदी में
- Pair Of Linear Equations In Two Variables Class 10 Ex 3.6
- प्रश्नावली 3.6 का हल हिंदी में
- Pair Of Linear Equations In Two Variables Class 10 Ex 3.7
- प्रश्नावली 3.7 का हल हिंदी में
- Extra Questions for Class 10 Maths Linear Equations in Two Variables
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.1
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.1 are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Exercise 3.1
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 10 |
| Subject | Maths |
| Chapter | Chapter 3 |
| Chapter Name | Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables |
| Exercise | Ex 3.1 |
| Number of Questions Solved | 3 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
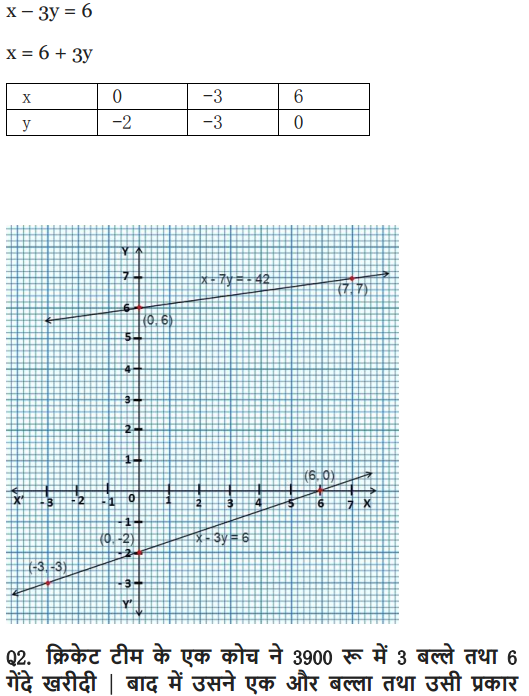
Ex 3.1 Class 10 Maths Question 1.
Aftab tells his daughter, “Seven years ago, I was seven times as old as you were then. Also, three years from now, I shall be three times as old as you will be”. Isn’t this interesting? Represent this situation algebraically and graphically.
Solution:
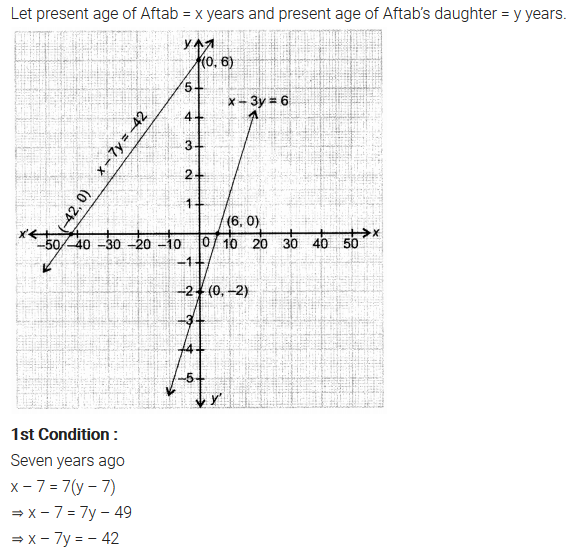
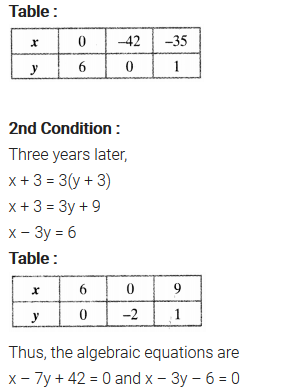
You can also download the free PDF of Ex 3.1 Class 10 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables NCERT Solutions or save the solution images and take the print out to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
Download NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables PDF
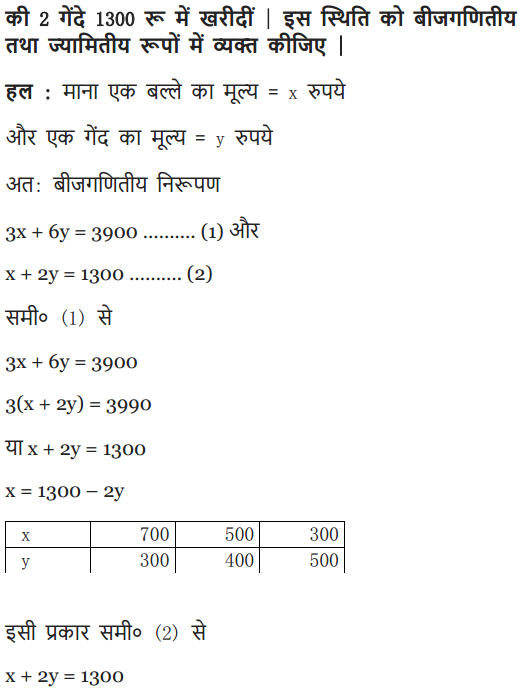
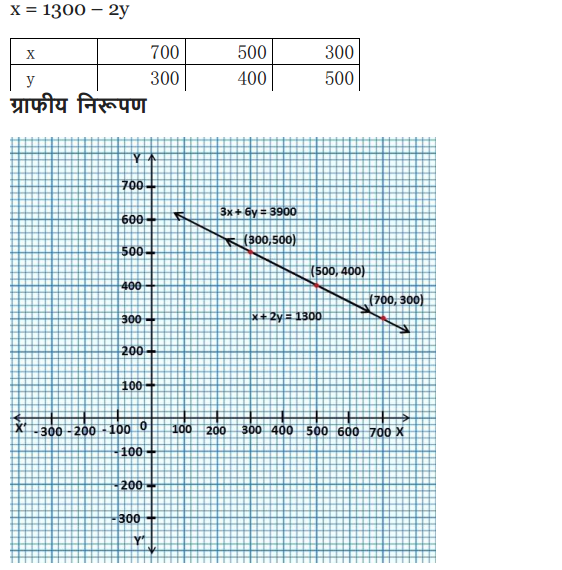
Ex 3.1 Class 10 Maths Question 2.
The coach of a cricket team buys 3 bats and 6 balls for ₹ 3900. Later, she buys another bat and 3 more balls of the same kind for ₹1300. Represent this situation algebraically and geometrically.
Solution:
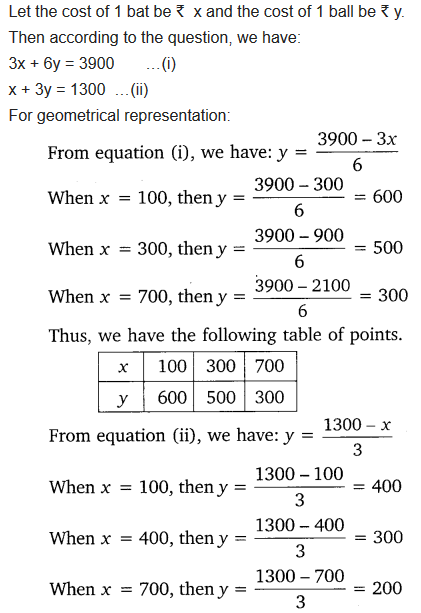
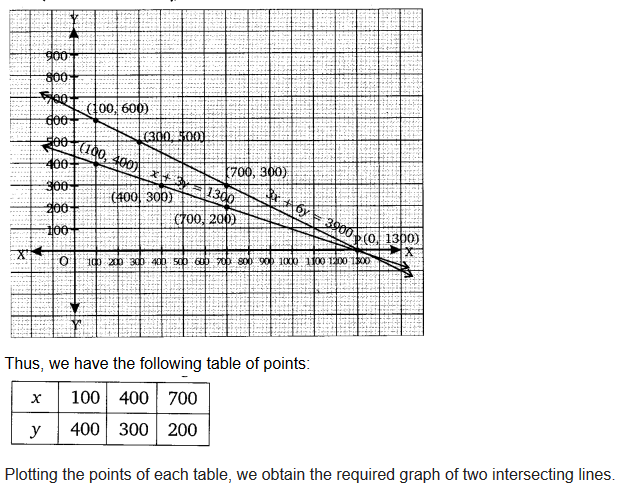
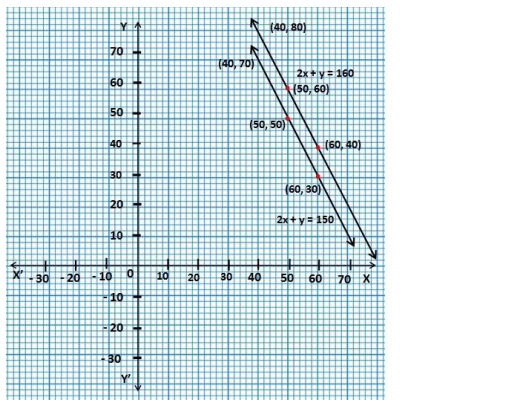
Ex 3.1 Class 10 Maths Question 3.
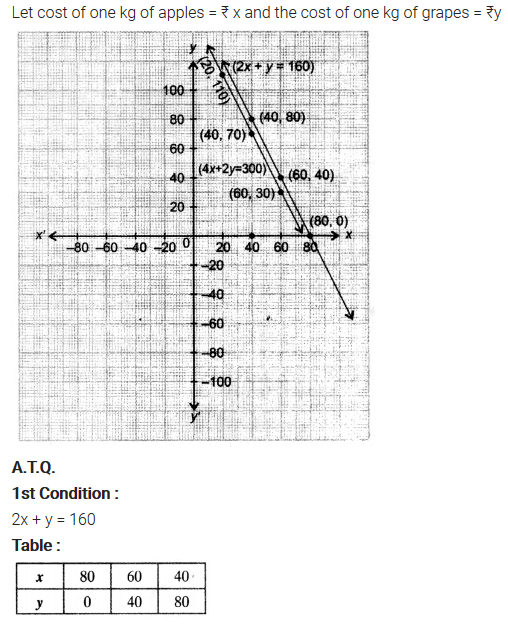
The cost of 2 kg of apples and 1 kg of grapes on a day was found to be ₹160. After a month, the cost of 4 kg of apples and 2 kg of grapes is ₹300. Represent the situation algebraically and geometrically.
Solution:

Class 10 Maths Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Mind Map
System of a Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
An equations of the form Ax + By + C = 0 is called a linear equation in two variables x and y where A, B, C are real numbers.
Two linear equations in the same two variables are called a pair of linear equations in two variables. Standard form of linear equations in two variables.
a1x + b1y + c1 = 0, a2x + b2y + c1 = 0
where a1, a2, b1, b2, c1, c2 are real numbers such that
![]()
Representation of Linear Equation In Two Variables
Every linear equation in two variables graphically represents a line and each solution (x, y) of a linear equation in two variables, ax + by + c = 0, corresponds to a point on the line representing the equation, and vice versa.
Ploting Linear Equation in Two Variables on the Graph
There are infinitely many solutions of each linear equation. So, we choose at least any two values of one variable & get the value of other variable by substitution, i.e; Consider; Ax + By + C = 0 We can write the above linear equation as:
![]()
Here, we can choose any values of x & can find corresponding values of y.
After getting the values of (x, y) we plot them on the graph thereby getting the line representing Ax + By + C = 0.
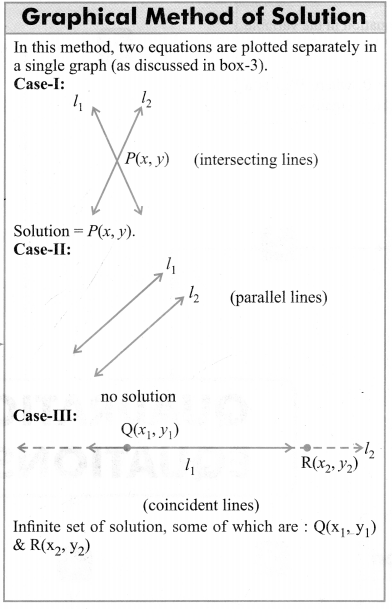
Method of Solution of a Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
Coordinate of the point (x, y) which satisfy the system of pair of linear equations in two variables is the required solution. This is the point where the two lines representing the two equations intersect each other.
There are two methods of finding solution of a pair of Linear equations in two variables.
(1) Graphical Method : This method is less convenient when point representing the solution has non-integral co-ordinates.
(2) Algebraic Method : This method is more convenient when point representing the solution has non-integral co-ordinates.
This method is further divided into three methods:
(i) Substitution Method,
(ii) Elimination Method and
(iii) Cross Multiplication Method.
Consistency and Nature of the Graphs
Consider the standard form of linear equations in two variables.
a1x + b1y + C1 = 0; a2x + b2y + c2 = 0
While solving the above system of equation following three cases arise.
(i) If a1a2≠b1b2; system is called consistent, having unique solution and pair of straight lines representing the above equations intersect at one point only
(ii) If a1a2=b1b2=c1c2 ; system is called dependent and have infinetly many solution. Pair of lines representing the equations coincide.
(iii) If a1a2=b1b2≠c1c2; system is called inconsistent and has no solution. Pair of lines representing the equations are parallel or do not intersect at any point.
Algebraic Method of Solution
Consider the following system of equation
a1x + b1y + c1 =0; a2x + b2y + c1 =0
There are following three methods under Algebraic method to solve the above system.
(i) Substitution method
(a) Find the value of one variable, say y in terms of x or x in terms of y from one equation.
(b) Substitute this value in second equation to get equation in one variable and find solution.
(c) Now substitute the value/solution so obtained in step (b) in the equation got in step (a).
(ii) Elimination Method
(a) If coefficient of any one variable are not same in both the equation multiply both the equation with suitable non-zero constants to make coefficient of any one variable numerically equal.
(b) Add or subtract the equations so obtained to get equation in one variable and solve it.
(c) Now substitute the value of the variable got in the above step in either of the original equation to get value of the other variable.
(iii) Cross multiplication method
For the pair of Linear equations intwo variables:
a1x + b1y + C1 = 0
a2x + b2y + c2 = 0
Consider the following diagram.
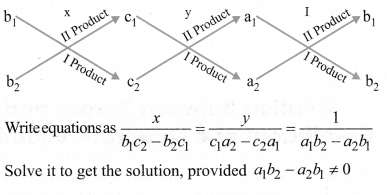
Solve it to get the solution, provided a1b2 – a2b1 ≠ 0
Equations Reducible to a Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
Sometimes pair of equations are not linear (or not in standard form), then they are altered so that they reduce to a pair of linear equations in standard form.
For example;
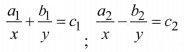
Here we substitute 1x = p & frac{1}{y} = q, the above equations reduces to:
a1p + b1q = c1 ; a2p – b2q = c2
Now we can use any method to solve them.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Pairs of Linear Equations in Two Variables (Hindi Medium) Ex 3.1